What Countries Do The Andes Run Through
ghettoyouths
Dec 03, 2025 · 9 min read
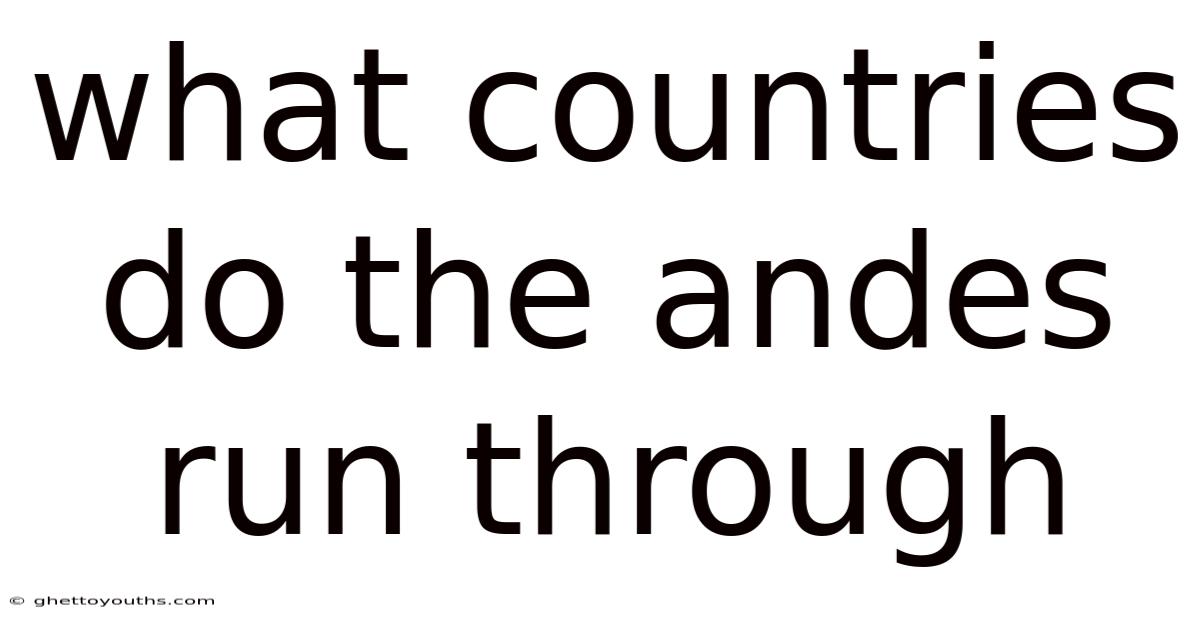
Table of Contents
The Andes Mountains, a colossal spine of rock and ice, dominate the western edge of South America. More than just a mountain range, the Andes are a dynamic ecosystem, a cradle of ancient civilizations, and a crucial determinant of climate. This magnificent range stretches for approximately 7,000 kilometers (4,300 miles), making it the longest continental mountain range in the world. Understanding which countries the Andes traverse is essential to grasping the geographical, cultural, and environmental significance of this natural wonder.
The Andes Mountains run through seven South American countries, shaping their landscapes, influencing their cultures, and impacting their economies. These countries are: Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, Chile, and Argentina. Each nation boasts unique sections of the Andes, characterized by distinct geological features, biodiversity, and human adaptations.
Andes Countries: A Detailed Overview
Let's delve into each of the seven countries the Andes run through, highlighting key aspects of the range within their borders:
1. Venezuela:
- Andean Presence: The Andes Mountains begin their journey in Venezuela, specifically in the southwestern region of the country. This northernmost portion of the range is known as the Cordillera de Mérida.
- Key Features: The Venezuelan Andes are characterized by high peaks, deep valleys, and glacial formations. Pico Bolívar, the highest peak in Venezuela, is located in this range, reaching an elevation of approximately 4,978 meters (16,332 feet).
- Ecological Significance: The Cordillera de Mérida is home to a diverse array of flora and fauna, including the spectacled bear, the Andean condor, and various endemic plant species.
- Cultural Impact: The Andean region of Venezuela is steeped in history and tradition, with indigenous communities maintaining their cultural heritage amidst the rugged terrain.
2. Colombia:
- Andean Presence: As the Andes extend into Colombia, they split into three distinct ranges, known as the Cordillera Occidental (Western Range), Cordillera Central (Central Range), and Cordillera Oriental (Eastern Range).
- Key Features: The Colombian Andes are characterized by volcanic peaks, fertile valleys, and diverse ecosystems. Nevado del Ruiz, a prominent volcano in the Cordillera Central, is known for its significant glacial cover.
- Ecological Significance: Colombia's Andean region is a biodiversity hotspot, harboring a vast array of plant and animal species, including the Andean cloud forest, home to numerous endemic orchids, bromeliads, and hummingbirds.
- Cultural Impact: The Colombian Andes have played a crucial role in the country's history and development, serving as a center for agriculture, mining, and trade. The city of Bogotá, the capital of Colombia, is located in the Cordillera Oriental.
3. Ecuador:
- Andean Presence: Ecuador lies entirely within the Andes Mountains, with two main ranges running north to south: the Cordillera Occidental and the Cordillera Real (Eastern Range).
- Key Features: The Ecuadorian Andes are renowned for their towering volcanoes, including Chimborazo, the highest point on Earth when measured from the Earth's center, and Cotopaxi, one of the world's highest active volcanoes.
- Ecological Significance: The Andean highlands of Ecuador are home to unique ecosystems, such as the páramo, a high-altitude grassland characterized by tussock grasses, cushion plants, and hardy shrubs.
- Cultural Impact: The Ecuadorian Andes have a rich indigenous heritage, with communities preserving their languages, customs, and traditional agricultural practices. The city of Quito, the capital of Ecuador, is nestled in a high Andean valley.
4. Peru:
- Andean Presence: The Andes Mountains dominate the landscape of Peru, running the length of the country and influencing its climate, geography, and culture.
- Key Features: The Peruvian Andes are characterized by their immense scale, with towering peaks, deep canyons, and extensive plateaus. Huascarán, the highest peak in Peru, reaches an elevation of approximately 6,768 meters (22,205 feet).
- Ecological Significance: The Peruvian Andes are home to a wide range of ecosystems, from the arid coastal deserts to the lush cloud forests of the eastern slopes. The region is known for its biodiversity, including the vicuña, the Andean condor, and various species of orchids.
- Cultural Impact: The Peruvian Andes have been the cradle of ancient civilizations, including the Inca Empire, which built impressive cities and agricultural terraces in the rugged terrain. Machu Picchu, the iconic Inca citadel, is located high in the Andes Mountains.
5. Bolivia:
- Andean Presence: Bolivia lies entirely within the Andes Mountains, with the range splitting into two main cordilleras: the Cordillera Occidental and the Cordillera Oriental.
- Key Features: The Bolivian Andes are characterized by high plateaus, volcanic peaks, and salt flats. The Altiplano, a vast high-altitude plateau, is one of the most distinctive features of the Bolivian Andes.
- Ecological Significance: The Bolivian Andes are home to unique ecosystems, such as the puna, a high-altitude grassland characterized by hardy grasses, shrubs, and cushion plants. Lake Titicaca, the highest navigable lake in the world, is located on the border between Bolivia and Peru.
- Cultural Impact: The Bolivian Andes have a rich indigenous heritage, with communities preserving their languages, customs, and traditional agricultural practices. The city of La Paz, the administrative capital of Bolivia, is located in a deep canyon in the Andes Mountains.
6. Chile:
- Andean Presence: The Andes Mountains form the eastern border of Chile, running the length of the country and serving as a natural barrier between Chile and Argentina.
- Key Features: The Chilean Andes are characterized by their volcanic peaks, glaciers, and arid landscapes. Ojos del Salado, the highest volcano in the world, is located on the border between Chile and Argentina.
- Ecological Significance: The Chilean Andes are home to a wide range of ecosystems, from the hyper-arid Atacama Desert to the temperate rainforests of Patagonia. The region is known for its biodiversity, including the Andean flamingo, the guanaco, and various species of cacti.
- Cultural Impact: The Chilean Andes have played a significant role in the country's history and development, serving as a source of minerals, water, and energy. The region is also home to indigenous communities who have adapted to the harsh environment.
7. Argentina:
- Andean Presence: The Andes Mountains form the western border of Argentina, running the length of the country and serving as a natural barrier between Argentina and Chile.
- Key Features: The Argentine Andes are characterized by their towering peaks, glaciers, and arid landscapes. Aconcagua, the highest peak in the Americas, is located in the Argentine Andes, reaching an elevation of approximately 6,961 meters (22,838 feet).
- Ecological Significance: The Argentine Andes are home to a wide range of ecosystems, from the high-altitude deserts to the temperate forests of Patagonia. The region is known for its biodiversity, including the Andean condor, the puma, and various species of wildflowers.
- Cultural Impact: The Argentine Andes have played a significant role in the country's history and development, serving as a source of minerals, water, and energy. The region is also home to indigenous communities who have adapted to the harsh environment.
The Andes: A Comprehensive Overview
The Andes Mountains are more than just a geographical feature; they are a complex system that influences the climate, ecology, and culture of South America.
- Formation: The Andes were formed by the subduction of the Nazca Plate beneath the South American Plate. This process, which began millions of years ago, has resulted in the uplift of the mountains and the formation of volcanoes.
- Geology: The Andes are composed of a variety of rock types, including igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks. The mountains are also characterized by fault lines, folds, and other geological features.
- Climate: The Andes Mountains have a significant impact on the climate of South America. The mountains act as a barrier to air masses, creating distinct climate zones on either side of the range. The western slopes of the Andes are generally arid, while the eastern slopes are more humid.
- Hydrology: The Andes Mountains are the source of many of South America's major rivers, including the Amazon, the Orinoco, and the Paraná. The mountains also contain numerous lakes, glaciers, and wetlands.
Trends & Recent Developments
- Climate Change Impacts: The Andes Mountains are highly vulnerable to the effects of climate change. Glaciers are melting at an accelerated rate, threatening water supplies and increasing the risk of floods. Changes in precipitation patterns are also impacting agriculture and ecosystems.
- Mining and Resource Extraction: The Andes Mountains are rich in minerals and other resources, leading to increased mining activity. This has resulted in environmental degradation, social conflicts, and impacts on indigenous communities.
- Tourism and Recreation: The Andes Mountains are a popular destination for tourists and outdoor enthusiasts. Hiking, climbing, skiing, and other activities attract visitors from around the world. However, tourism can also have negative impacts on the environment and local communities.
- Conservation Efforts: There are numerous conservation efforts underway to protect the Andes Mountains. These efforts include the establishment of national parks and protected areas, the promotion of sustainable tourism, and the implementation of environmental regulations.
Tips & Expert Advice
- Respect the Environment: When visiting the Andes Mountains, it is essential to respect the environment. Pack out all trash, stay on marked trails, and avoid disturbing wildlife.
- Acclimatize to the Altitude: The high altitude of the Andes Mountains can cause altitude sickness. It is important to acclimatize gradually by spending time at lower elevations before ascending to higher altitudes.
- Support Local Communities: When traveling in the Andes Mountains, support local communities by buying local products and services. This can help to boost the local economy and preserve cultural traditions.
- Learn About the Culture: The Andes Mountains have a rich cultural heritage. Take the time to learn about the history, customs, and traditions of the people who live in the region.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
- Q: What is the highest peak in the Andes Mountains?
- A: Aconcagua, located in Argentina, is the highest peak in the Andes Mountains, reaching an elevation of approximately 6,961 meters (22,838 feet).
- Q: What is the largest lake in the Andes Mountains?
- A: Lake Titicaca, located on the border between Bolivia and Peru, is the largest lake in the Andes Mountains and the highest navigable lake in the world.
- Q: What is the driest desert in the Andes Mountains?
- A: The Atacama Desert, located in Chile, is one of the driest deserts in the world and is found within the Andes Mountains.
- Q: What are some of the major cities located in the Andes Mountains?
- A: Some of the major cities located in the Andes Mountains include Bogotá (Colombia), Quito (Ecuador), La Paz (Bolivia), and Cusco (Peru).
Conclusion
The Andes Mountains are a defining feature of South America, running through seven countries and influencing the lives of millions of people. From Venezuela to Argentina, the Andes shape landscapes, dictate climate, and foster unique cultures. Understanding the geographical extent and ecological significance of the Andes is crucial for appreciating the complexity and importance of this magnificent mountain range. As climate change and development pressures intensify, it is more important than ever to prioritize the conservation and sustainable management of the Andes Mountains for the benefit of future generations.
What are your thoughts on the impact of climate change on the Andean glaciers? Are you interested in exploring the ancient Inca trails within the Peruvian Andes?
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Countries Do The Andes Run Through . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.