What Does The M Stand For In Y Mx B
ghettoyouths
Nov 29, 2025 · 10 min read
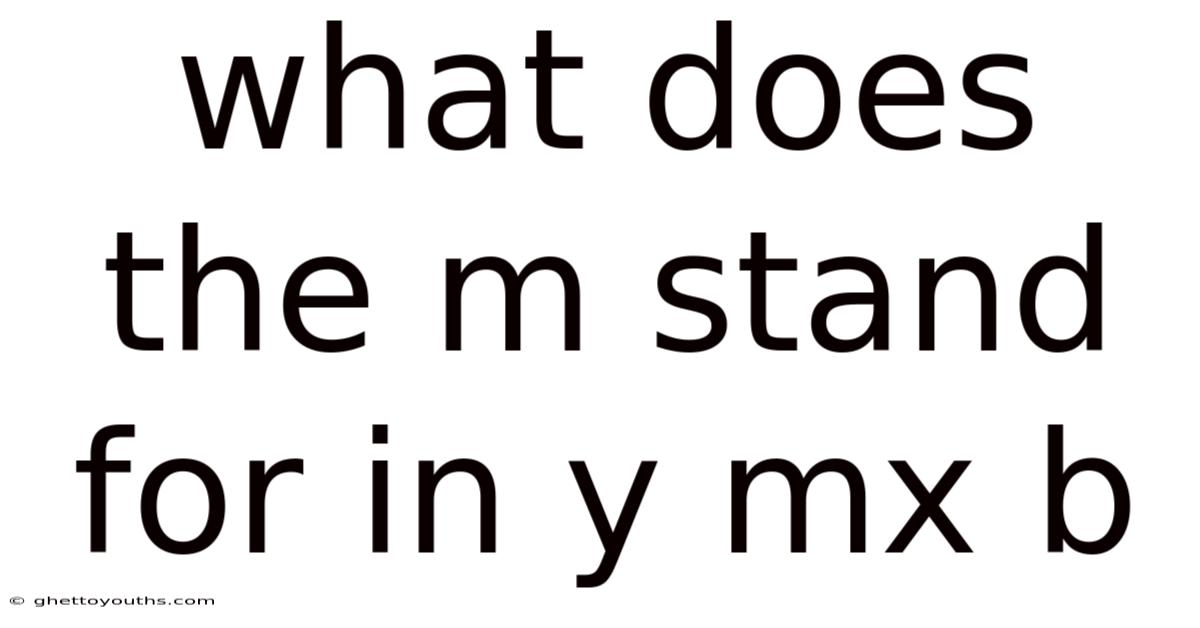
Table of Contents
Alright, let's craft a comprehensive and engaging article answering the question: "What does the 'm' stand for in y = mx + b?". This article will cover the concept of slope, its significance in linear equations, and related insights.
Unveiling the Mystery: What 'm' Truly Means in the Equation y = mx + b
The world of algebra can sometimes seem like a maze of symbols and formulas. But within this intricate system, lies a profound elegance and practical power. One of the most fundamental equations in algebra is the slope-intercept form of a linear equation: y = mx + b. While many people become familiar with this equation, understanding what each element represents is essential for truly grasping its significance. This article is dedicated to one particular element: 'm'. We will delve deep into what 'm' stands for, its geometric interpretation, and its importance in various mathematical and real-world applications.
We'll explore the foundations of linear equations, unravel the mystery behind 'm', discuss its relationship to the steepness and direction of a line, and provide real-world examples. Whether you're a student grappling with algebra or simply curious about the mathematical principles that shape our world, this guide will equip you with a comprehensive understanding of the slope-intercept form and the crucial role 'm' plays within it.
Introduction to Linear Equations
Before we dive into the specifics of 'm', let's establish a firm understanding of linear equations. A linear equation is an algebraic equation in which each term is either a constant or the product of a constant and a single variable. In simpler terms, it's an equation that, when graphed, forms a straight line.
The general form of a linear equation is Ax + By = C, where A, B, and C are constants, and x and y are variables. However, the slope-intercept form, y = mx + b, is particularly useful because it directly reveals two key characteristics of the line: its slope ('m') and its y-intercept ('b'). Understanding these characteristics allows us to quickly visualize and analyze the behavior of the line.
The Slope-Intercept Form: y = mx + b
Let's break down each component of the equation y = mx + b:
- y: Represents the dependent variable, which means its value depends on the value of x. Graphically, y corresponds to the vertical axis.
- x: Represents the independent variable. Its value can be chosen freely, and it affects the value of y. Graphically, x corresponds to the horizontal axis.
- m: This is what we're here to discuss! 'm' represents the slope of the line. The slope describes how steeply the line rises or falls and its direction.
- b: Represents the y-intercept of the line. This is the point where the line crosses the y-axis (when x = 0).
Decoding 'm': The Meaning of Slope
'm' stands for the slope of the line. Slope is a measure of the steepness and direction of a line on a graph. It quantifies how much the y-value changes for every unit change in the x-value. In simpler terms, it tells you how much the line goes up (or down) as you move from left to right.
The slope is often described as "rise over run," which can be expressed mathematically as:
m = (change in y) / (change in x) = Δy / Δx
Where Δy represents the change in the y-coordinate and Δx represents the change in the x-coordinate between two points on the line.
Calculating the Slope: Rise Over Run
To calculate the slope, you need two points on the line. Let's say you have two points, (x1, y1) and (x2, y2). Then the slope 'm' can be calculated as:
m = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1)
For example, if you have the points (1, 3) and (4, 9), the slope would be:
m = (9 - 3) / (4 - 1) = 6 / 3 = 2
This means that for every 1 unit increase in x, the y-value increases by 2 units. The line rises steadily as you move from left to right.
Positive, Negative, Zero, and Undefined Slopes
The slope of a line can be positive, negative, zero, or undefined, each indicating a different characteristic of the line:
- Positive Slope (m > 0): The line slopes upwards from left to right. As x increases, y also increases.
- Negative Slope (m < 0): The line slopes downwards from left to right. As x increases, y decreases.
- Zero Slope (m = 0): The line is horizontal. The y-value remains constant regardless of the value of x. This represents a function where y = b.
- Undefined Slope: The line is vertical. The x-value remains constant regardless of the value of y. The slope is undefined because the change in x (run) is zero, and division by zero is not allowed.
The Geometric Interpretation of 'm'
The slope 'm' has a clear geometric interpretation on the graph. Imagine a right triangle formed by any two points on the line, where the line itself is the hypotenuse. The "rise" (Δy) is the vertical leg of the triangle, and the "run" (Δx) is the horizontal leg. The slope is simply the ratio of the rise to the run.
A larger absolute value of 'm' indicates a steeper line. A slope of 5 is steeper than a slope of 2. A negative slope indicates that the line is descending, while a positive slope indicates that the line is ascending.
The Relationship Between Slope and Angle of Inclination
The slope is also directly related to the angle of inclination of the line. The angle of inclination (θ) is the angle that the line makes with the positive x-axis, measured counterclockwise. The slope 'm' is equal to the tangent of the angle of inclination:
m = tan(θ)
This relationship allows us to determine the angle of inclination if we know the slope, and vice versa. For example, if the slope is 1, then the angle of inclination is arctan(1) = 45 degrees.
Why is Understanding Slope Important?
Understanding slope is crucial for several reasons:
- Predicting Behavior: Slope allows us to predict how the dependent variable (y) will change in response to changes in the independent variable (x).
- Modeling Real-World Phenomena: Many real-world relationships can be modeled using linear equations. Understanding slope helps us interpret these models and make predictions.
- Calculus Foundation: The concept of slope forms the basis for calculus concepts like derivatives, which measure the instantaneous rate of change of a function.
- Problem Solving: Knowing the slope and y-intercept makes it much easier to solve problems related to linear equations, such as finding the equation of a line given certain points or determining where two lines intersect.
Real-World Applications of Slope
Slope isn't just a mathematical concept; it has numerous applications in the real world:
- Construction: Architects and engineers use slope to design roofs, ramps, and roads. For example, the slope of a roof affects how well it sheds water and snow. The slope of a ramp determines its accessibility for people with disabilities.
- Navigation: Pilots and sailors use slope to calculate their descent or ascent angles.
- Economics: Economists use slope to measure the marginal propensity to consume, which represents the change in consumer spending for every unit change in income.
- Physics: Physicists use slope to calculate the velocity of an object, which is the rate of change of its position over time.
- Finance: Financial analysts use slope to determine the rate of return on investment over a given period. A steeper slope would indicate a faster rate of return.
Tren & Perkembangan Terbaru (Trends & Recent Developments)
While the fundamental concept of slope remains constant, its application and interpretation are constantly evolving with the development of new technologies and analytical tools.
- Data Analysis and Machine Learning: In data analysis and machine learning, the concept of slope is extended to multi-dimensional spaces and non-linear functions. Gradient descent, a widely used optimization algorithm, relies on finding the "slope" of a cost function to minimize errors and improve model accuracy.
- Interactive Graphing Tools: Modern graphing calculators and online tools like Desmos and GeoGebra allow users to visualize and manipulate linear equations in real-time. This has made it easier for students and professionals to explore the effects of changing the slope and y-intercept on the graph of a line.
- Statistical Modeling: Linear regression, a statistical technique used to model the relationship between variables, is based on the concept of slope. Recent advancements in statistical software have made it easier to perform linear regression analysis and interpret the results.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS applications use slope to analyze terrain, predict landslides, and plan infrastructure projects. High-resolution elevation data and advanced algorithms have improved the accuracy and efficiency of slope analysis in GIS.
Tips & Expert Advice
Here are some tips and expert advice to help you master the concept of slope:
- Visualize the Line: When you see a linear equation, try to visualize the line on a graph. This will help you understand the relationship between the slope and the direction of the line.
- Practice Calculating Slope: Practice calculating the slope using different sets of points. This will help you become more comfortable with the formula and the concept.
- Use Graphing Tools: Use graphing calculators or online tools to explore the effects of changing the slope and y-intercept on the graph of a line.
- Relate to Real-World Examples: Try to relate the concept of slope to real-world examples. This will help you understand the practical significance of slope and its applications.
- Pay Attention to the Sign: Always pay attention to the sign of the slope. A positive slope indicates an increasing line, while a negative slope indicates a decreasing line.
- Understand the Units: When applying slope in real-world problems, make sure you understand the units of the variables and the slope. For example, if y represents distance in meters and x represents time in seconds, then the slope represents velocity in meters per second.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
- Q: What is the difference between slope and y-intercept?
- A: Slope measures the steepness and direction of a line, while the y-intercept is the point where the line crosses the y-axis.
- Q: Can a line have more than one slope?
- A: No, a straight line has a constant slope throughout its entire length.
- Q: What does it mean if the slope is undefined?
- A: An undefined slope indicates a vertical line.
- Q: How do I find the slope of a line if I only have one point?
- A: You need at least two points to calculate the slope of a line.
- Q: Is the slope always a whole number?
- A: No, the slope can be any real number, including fractions and decimals.
Conclusion
In the equation y = mx + b, 'm' is much more than just a letter; it's the key to understanding the behavior of a line. It quantifies the steepness and direction, allowing us to predict how the dependent variable changes with respect to the independent variable. From construction and navigation to economics and physics, the concept of slope permeates numerous aspects of our world.
By understanding the meaning of 'm', you gain a powerful tool for analyzing and interpreting linear relationships. So, the next time you encounter the equation y = mx + b, remember that 'm' is the slope, and it's telling you a story about the line's inclination and direction.
How do you see slope applied in your everyday life? Are you ready to tackle more complex mathematical concepts building upon this foundation?
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Does The M Stand For In Y Mx B . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.